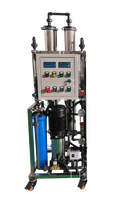
AMANDA has 28 years of water treatment industry experience and 16 years of export experience.,it is a production and distribution company of water treatment products, production:UV sterilizer/Ozone generator/Industry and Household purification system;distribution:FRP tank/RUNXIN valve/ Water distributor/RO membrane/Industry RO membrane housing/Filter cartridge /Filter housing .